Liver cancer
Liver cancer is one of the commonest causes of cancer related deaths in the world. The cancer may originate from the liver itself called Hepatocellular cancer (HCC), arise from the bile ducts called cholangiocarcinoma, or may be as a result of spread from other organs (Metastatic cancer). The HCC usually develops in an already diseased liver (cirrhosis – stiff and shrunken liver). The cirrhosis in turn may be a result of longstanding infection (hepatitis B, hepatitis C ), Alcohol consumption, fatty liver disease, congenital liver diseases and so on.
The common symptoms are vague abdominal discomfort or pain, jaundice and ascites. However, patients may be asymptomatic till the disease is very advanced. Ultrasound, CT scan or blood tests are usually sufficient for the diagnosis.
Treatment of HCC depends on the nature and stage of the cancer. In early stage, surgical resection of the tumour is the best option. However, most patients, at the time of the diagnosis, have advanced stage disease. In such patients, depending upon the tumour size, the treatment options include Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), Trans arterial chemo embolization (TACE) and Trans Arterial Radio embolization (TARE). In early stage of HCC, these treatment options may be curative on their own. However, in advanced disease most of these treatment methods reduce the size and growth of tumour and act like a bridge for surgical treatment.
Surgery: The surgical resection is the best treatment which is done in early stage of the cancer. However, in the advanced stage of the disease, the cancer is down-staged by various treatment methods and, thereafter, surgery may be performed. If the liver has cirrhosis (stiff and shrunken) in addition to the liver cancer, then liver transplant is often needed. It involves replacing the diseased liver with a new liver from a healthy donor.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): A needle like electrode is inserted through the skin into the tumour under the guidance of the USG or CT scan. The needle generates heat at its tip which, in turn, causes heating of the tumour. This results in tumour necrosis (death of the tumour) while the normal tissues are least affected. This procedure doesn’t need an open surgery. It is done under local anaesthesia or mild sedation and the patient is discharged the next day.
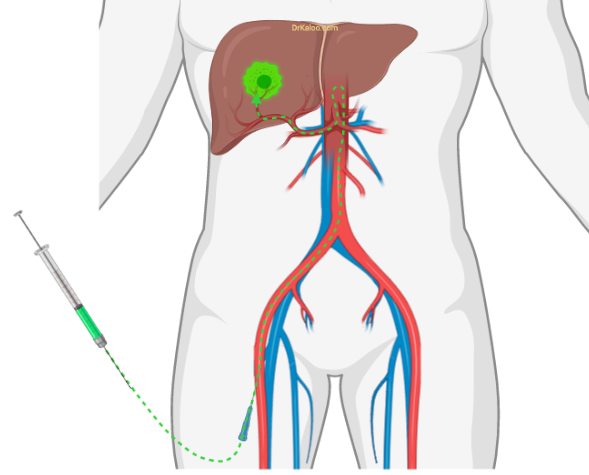
Trans- arterial chemo Embolization (TACE): Angiography of the liver is done with a thin thread like long plastic tube (called Catheter) placed in an artery in the groin. Cancer killing medicine (chemotherapy) is injected such that the medicine is deposited into the tumour only while preserving the rest of the normal liver. With this method the medicine reaches the tumour in highest concentrations for highest benefit, while at the same time the side effects on the body of the patient are least.
Trans Arterial Radio Embolization (TARE): This is similar to TACE, with the difference that instead of chemotherapy, small radioactive particles (Yattrium 90) are injected into the tumour through the catheter. The death of the tumour cells results from the radiation emitted by the radioactive particles while preserving the normal liver. TARE is useful even in very advanced disease stages of HCC
In summary, the liver cancer is a common health problem all over the world with various treatment options available. The best results are achieved with early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach with combined efforts of Surgeons, interventional Radiologists, medical Hepatologists, and Oncologists.
Quick Links
- Know your doctor
- Liver Cancer (RFA/TACE/TARE)
- TIPS/DIPS(Cirrhosis)
- Biliary Diseases (PTBD/Stent)
- Dialysis Access (Permacath/Fistula-plasty)
- Biopsy/FNAC
- Bronchial artery embolisation
- Uterine Artery embolisation
- Prostate Embolisation (BPH)
- Varicocele treatment
- Varicose Veins
- Picture Gallery
- Video Gallery
Quick Links
- Know your doctor
- Liver Cancer (RFA/TACE/TARE)
- TIPS/DIPS(Cirrhosis)
- Biliary Diseases (PTBD/Stent)
- Dialysis Access (Permacath/Fistula-plasty)
- Biopsy/FNAC
- Bronchial artery embolisation
- Uterine Artery embolisation
- Prostate Embolisation (BPH)
- Varicocele treatment
- Varicose Veins
- Picture Gallery
- Video Gallery




